Learning to ride a bicycle was one of the challenges we faced during our childhood. Initially, we start with the supporting wheel and with time we pedal on our own. Same goes for learning anything. First we need to gain the balance and make the base strong inorder to build our knowledge. So the hurdle is when do we know we can pedal on our own and even try some stunts?
Latest educational advancements focus on making learning application based and try to increase the practical efficiency of a concept. Bloom’s Taxonomy is a guide to teachers and educators for enhancing the learning techniques. It was originally developed by Benjamin Bloom. Learning and teaching objectives are divided into six levels in the form of a pyramid. The initial model was revised in 2001 by a group of researchers and theorists under the title A Taxonomy for teaching, learning and assessment.
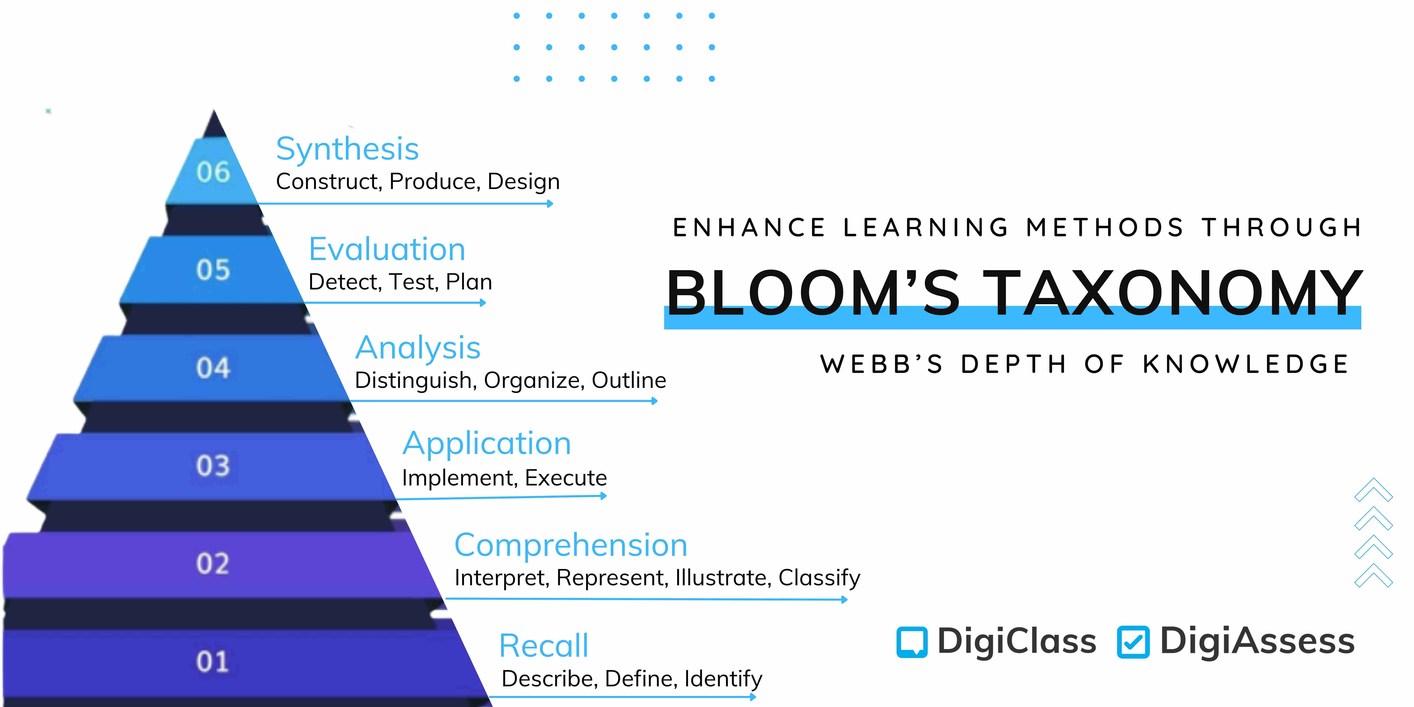
The six levels of the pyramid are as follows:
- Remember / Recall - can you recall the information?
- Understand / Comprehension - can you explain the idea?
- Apply / Application - can you use the idea or facts?
- Analyze / analysis - can you categorize or differentiate the various parts of the information?
- Evaluate / evaluation - can you decide or justify your decision?
- Create / synthesis - can you put the elements together to make something new?
So how can teachers implement these levels to their learning techniques? Each level can be incorporated into learning activities using verbs indicating each stage in the pyramid. The revised version of Bloom's Taxonomy incorporated verbs for defining each level of the learning pyramid.
The various verbs used during assessment preparation are:
1. REMEMBER / RECALL
Describe, define, identify
2. UNDERSTAND / COMPREHENSION
Interpret, represent, illustrate, classify
3. APPLY / APPLICATION
Implement, execute
4. ANALYZE / ANALYSIS
Distinguish, organize, outline
5. EVALUATE / EVALUATION
Detect, test, plan
6. CREATE / SYNTHESIS
Construct, produce, design
Teachers can use the lower levels for introducing a concept, and gradually move to the higher levels which allows higher order thinking. Then how can you implement these levels in your teaching? Teachers and educators can implement the levels in their assessments and activities by using "action words". Bloom’s taxonomy ensures the practical ability of every piece of information shared with the students and provides them the space to create new knowledge.
Let us understand these levels with an example:
- Remembering or recalling- learning new vocabulary
- Understand - categorizing the new words into different parts of speech
- Applying - using the words in a sentence
- Analyzing - understanding the different words and their origins
- Evaluating - deciding the parts of speech that are important for the sentence
- Creating - building a crossword for the words
While Bloom focussed on the various levels at which learning takes place, Dr. Norman Webb concentrated on the context or setting in which the students are required to apply their learning. According to this model, assessments should evaluate how deeply students understand a concept and how effectively they can use the information in real world scenarios.
The four level of Webb’s model are as follows:
- Acquired knowledge - recall and reproduction of facts or information
- Knowledge application - applying learned concepts to solve problems
- Analysis - involves planning, reasoning and strategic thinking.
- Augmentation - applying the learned concepts in real world contexts
Bloom and Webb developed strategic tools to make learning effective and developed methods to improve the assessment of knowledge acquired. These guides of teaching and learning show us how every information or idea that we learn can be used and applied in the real world. Each level of learning allows the students to move from understanding to higher order critical thinking.
bloomstaxonomywebbsdepthofknowledgeassessment softwareassessmentplatformdigiassessexam softwaredigital assessment systemeducationmodel